The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is a significant topic in the realm of internet technology. For CIOs, CTOs, and VPs/Directors of IT, Marketing, and Sales, understanding the nuances between these protocols is crucial for strategic planning and operational efficiency. Data scientists, analysts, and AI/ML engineers need to grasp these concepts. This will help them enhance data management and develop long-lasting solutions. This article compares IPv6 and IPv4, showing how they can benefit your organization.

On this page
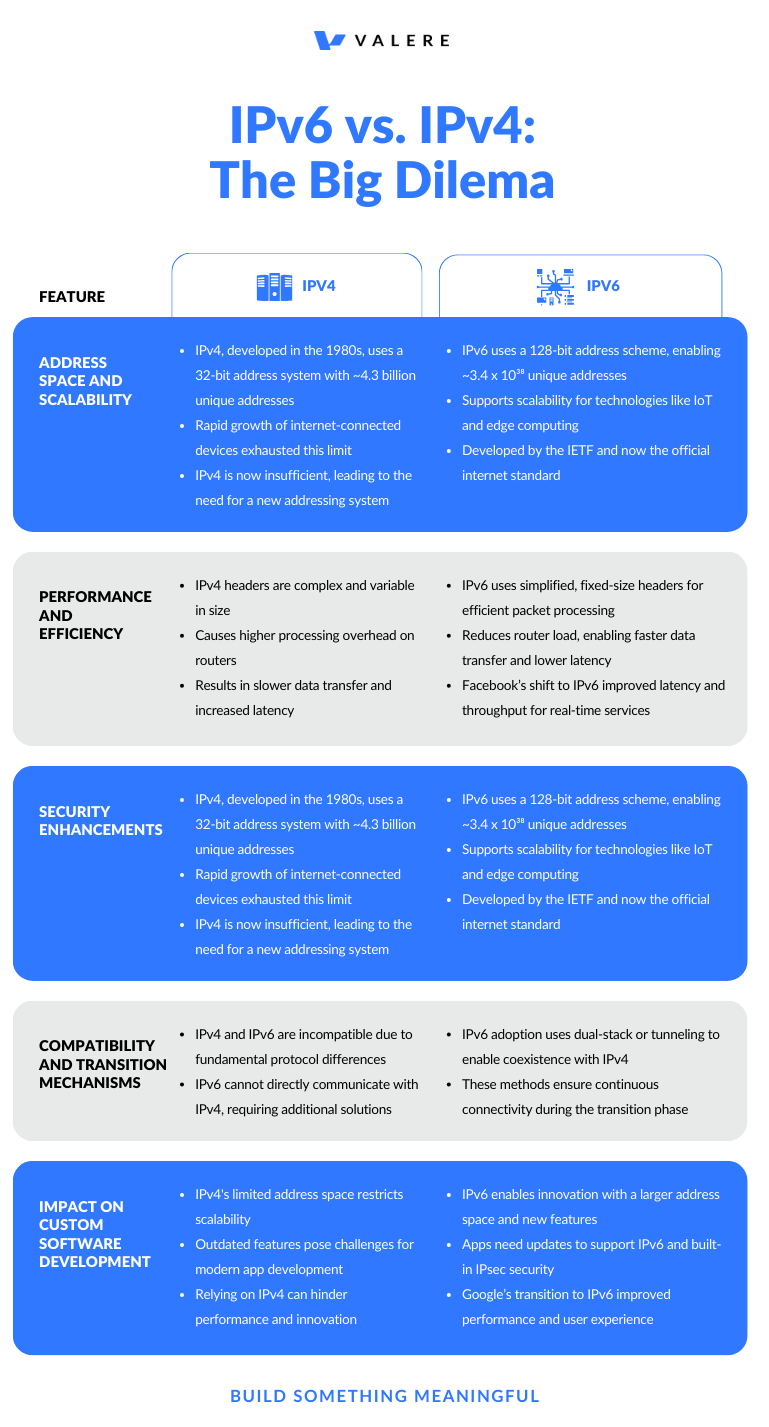
Address Space and Scalability
Performance and Efficiency
Security Enhancements
Compatibility and Transition Mechanisms
Impact on Custom Software Development
Conclusion
IPv4, created in the early 1980s, uses a 32-bit address scheme, allowing for approximately 4.3 billion unique addresses. The exponential growth of internet-connected devices has exhausted this limit, leading to the development of IPv6. IPv6 uses a 128-bit address scheme, offering an almost limitless number of unique IP addresses (3.4 x 10^38). This vast address space ensures scalability for future technologies like IoT and edge computing, which require numerous IP addresses.
The internet runs on a system called the Internet Protocol (IP) that gives devices an address to find each other. This system, like many things, gets full sometimes! IPv6 is the newest version of IP, designed to handle WAY more devices than the old system (IPv4). It was created by a group called the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) and is now the official standard for the internet.
IPv6 enhances performance through streamlined packet processing. Unlike IPv4, IPv6 headers are simplified and fixed in size, which reduces the processing overhead on routers. This efficiency can lead to faster data transfer rates and lower latency, which are critical for applications demanding high performance, such as AI/ML data processing and real-time analytics.
Case Study: Facebook's transition to IPv6 resulted in a noticeable improvement in performance metrics. They reported lower latency and higher throughput, which is particularly beneficial for their real-time services.
IPv6 was designed with security in mind. It incorporates IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) as a fundamental feature, providing confidentiality, integrity, and authentication of data. IPsec is easier to use with IPv6 than with IPv4, making communication more secure in the process.
Data Point: According to a study by the Internet Society, networks utilizing IPv6 showed a 25% reduction in the number of detected security threats compared to those using IPv4, thanks to the built-in security features.
Transitioning from IPv4 to IPv6 is not without challenges. IPv6 is not backward compatible with IPv4, necessitating dual-stack implementations or tunneling mechanisms during the transition period. These methods allow for the coexistence of both protocols, ensuring uninterrupted service during the gradual shift.
For software developers, the transition to IPv6 offers opportunities to innovate and optimize. Custom software needs to be designed or updated to support IPv6, ensuring compatibility and leveraging the benefits of the new protocol. This includes handling the larger address space, optimizing for IPv6-specific features, and ensuring security through built-in IPsec support.
Google developers found that updating their services for IPv6 was challenging but led to better performance and user experience.
Moving from IPv4 to IPv6 is more than just a technical upgrade. It is a strategic decision that provides important benefits like scalability, performance, and security for businesses today. For CIOs, CTOs, and IT leaders, planning and executing this transition can future-proof your infrastructure. Data scientists, analysts, and AI/ML engineers will benefit from the enhanced capabilities of IPv6 in handling large datasets and real-time processing.
To learn more, explore resources on the best practices for custom software development. You can also find information on strategies for transitioning to IPv6. Additionally, you can stay updated on the latest trends in network security.
Understanding the differences between IPv4 and IPv6 and their implications for your organization is a crucial step in maintaining a competitive edge in today's technology-driven landscape.

Share